
Photovoltaic cells and solar panels are two options for producing electricity that doesn't require additional energy costs. How do they work? And how much are they worth? This article will discuss what they are and how they are made.
Solar panels
A solar panel is made up of solar cells which convert light directly to electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect and is a physical and chemical process. This technology is increasingly being used in residential and commercial settings. It's a great way to produce electricity from renewable sources.
The panels are made up of many photovoltaics cells. These small pieces of silicon are sandwiched together. These cells are exposed to sunlight, which knocks out electrons and causes them to flow towards a conductive plate. The electricity produced is then passed through wires to a device called an inverter. The inverter transforms the direct current into an alternating current that can be used for powering homes and buildings.
Photovoltaic cells
Photovoltaic cells in solar panels convert light energy into electricity. They work by absorbing sunlight and transferring it into negatively charged particles within a material called electrons. This extra energy allows electrons through the material to flow as an electricity current. It can then extracted through conductive contacts metal, such grid-like lines on solar cells. These solar cells produce electricity that can be used to power homes and the electric grid.
Photovoltaics are solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity by using the photovoltaic process. The photons that are emitted from the sun's rays knock electrons from silicon atoms in the solar cells. These electrons can flow freely inside the cell and turn the light into electric power.
Manufacturing process
A series of steps are involved in making solar panels. To prevent shock or water from getting into the solar panel, the solar cells need to be laminated. Next, the solar cells are placed in an aluminum frame with a tedlar or mylar backsheet and a glass or plastic cover. The panels are then inspected for quality throughout production.
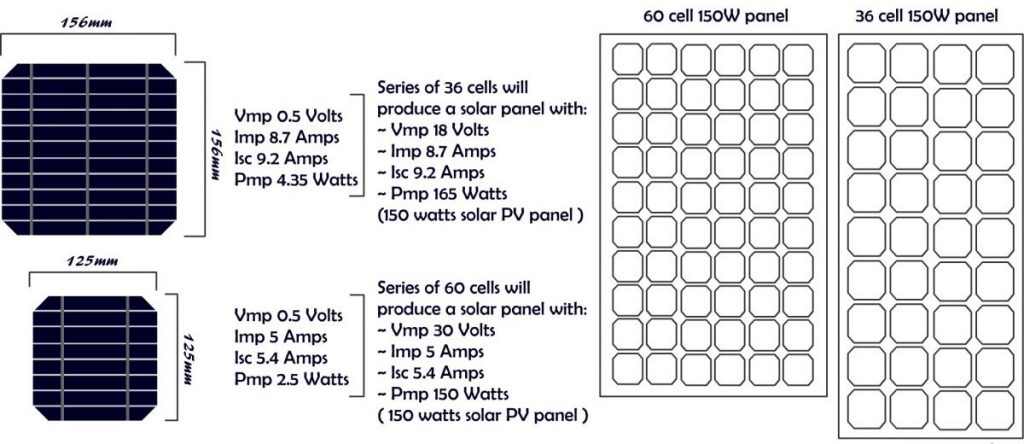
The solar cells are then soldered together. Next, they are subjected to more quality control testing and are sorted based on their power output. They are then connected using metal connectors. These solar cell are then assembled into a PV module, which consists of many similar cells. The cells are connected in a series, with one negative contact and one positive contact. Solar cells are manufactured with a standardized size, with 60 cells being the standard size for residential and commercial projects.
Cost
A variety of factors affect the price of solar panels or photovoltaic cell. These factors include how much sunshine a household receives, and how much electricity they use each month. For instance, a house with mainly gas appliances will use less power than one with mostly electrical appliances. Its efficiency is another factor that affects the cost of solar panels. You'll save more money if your panels are more efficient. Consider the roof space available to your home.
Solar panels are typically $0.30 per W. However, the larger the number of solar panels, the more expensive it will be. For an average 1,500 square foot home, 16 panels will be required to generate enough power for the electric consumption. Additional panels might be required if the home is situated in an area with shaded or east facing areas.
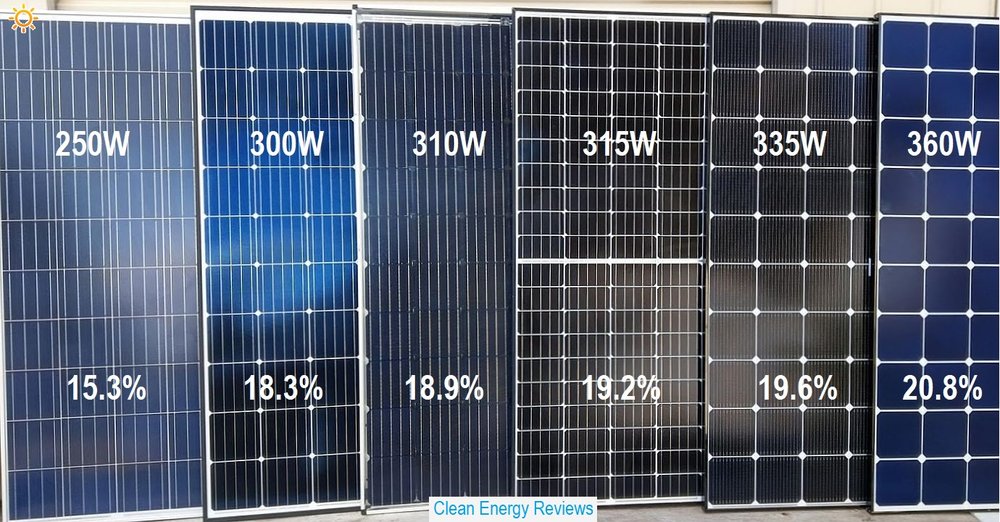
Efficiency
The efficiency of solar panels is a measure of how efficiently they convert sunlight to electricity. A solar panel with 100% efficiency, for example, would be capable of converting all sunlight into electrical energy. According to scientists solar efficiency refers to the ratio of solar energy produced to solar energy consumed.
The efficiency and type of solar cell used to make solar panels can have an impact on their effectiveness. For instance, some cells may be inefficient because they capture only a fraction of sunlight. Because sunlight has a spectrum, semiconductors can only absorb a small portion of what they see. The semiconductors may also reflect or absorb some light. These inefficiencies affect the efficiency of solar panels, and the systems they make up.